High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, silently afflicts countless individuals, posing significant health risks without manifesting obvious symptoms.
It’s a condition where the force of the blood against artery walls is too high, potentially leading to heart disease, stroke, and other health complications.
Recognizing the power of diet in this equation is a game-changer. Healthy eating not only serves as a foundational strategy for managing high blood pressure but also fortifies overall health.
This article delves into practical dietary adjustments that can keep your blood pressure in check.
From understanding the intricate relationship between food and hypertension to actionable advice on meal planning, you’re about to discover how the foods you choose impact your blood pressure and ways to harness this knowledge for better health.
As always, this articles serves as a guide. Please consult your family physician for more specified diagnosis.
Understanding High Blood Pressure
When discussing high blood pressure, or hypertension, it’s crucial to recognize it as a condition where the force of the blood against the artery walls is too high.
Over time, this excessive pressure can cause health problems, such as heart disease. Hypertension is often categorized into stages:
- Normal: systolic less than 120 mm Hg and diastolic less than 80 mm Hg
- Elevated: systolic between 120-129 mm Hg and diastolic less than 80 mm Hg
- Hypertension Stage 1: systolic between 130-139 mm Hg or diastolic between 80-89 mm Hg
- Hypertension Stage 2: systolic at least 140 mm Hg or diastolic at least 90 mm Hg
- Hypertensive crisis: systolic over 180 mm Hg and/or diastolic over 120 mm Hg
In Singapore, hypertension remains a pressing issue with one in four adults affected by the condition. The significance of this health challenge cannot be overstated, as it silently escalates the risk for severe complications without noticeable symptoms.
The risks associated with unmanaged hypertension are substantial, including:
- Heart disease: Strain on the heart leading to coronary artery disease and increased risk of heart attack.
- Stroke: Compromised blood flow to the brain due to narrowed or blocked arteries.
Recognizing the silent yet hazardous nature of hypertension underscores the importance of preventive measures and proactive management through lifestyle choices such as diet, which we will delve into next.
The Link Between Diet and Hypertension
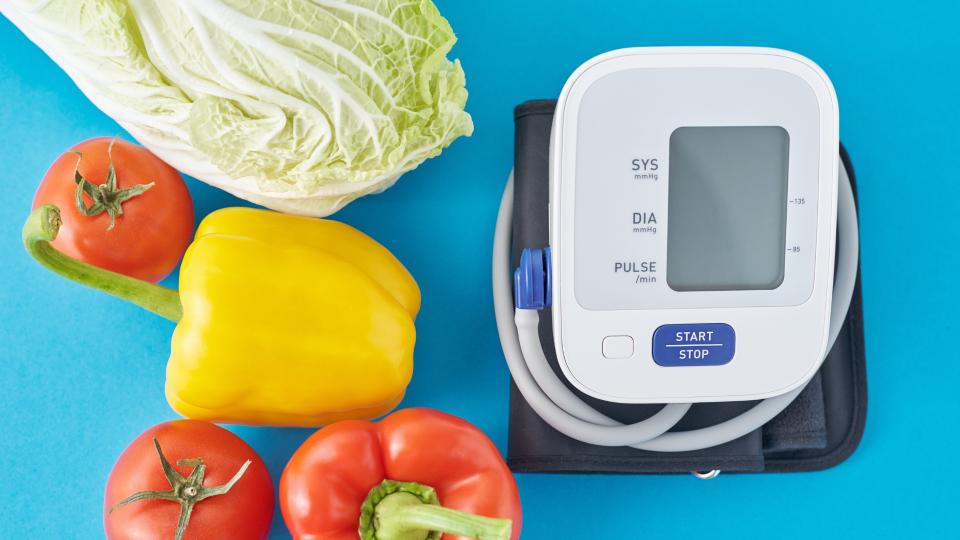

The food choices we make daily are not just about satisfying hunger; they have a substantial impact on our body’s physiological functions, including blood pressure regulation.
Scientific research has established a clear diet-hypertension relationship, revealing that certain nutrients can exert significant influence on vascular health.
Certain dietary habits are known to contribute to the development of hypertension:
- High Salt Intake: An excess of sodium can cause the body to retain water, increasing the volume of blood in the bloodstream and consequently, blood pressure.
- Low Potassium Levels: Potassium helps balance the amount of sodium in your cells. A low potassium intake can lead to an accumulation of sodium in the blood.
- Saturated Fats and Cholesterol: These can cause the arteries to harden and narrow, increasing blood pressure.
- Alcohol Consumption: Regular heavy drinking can damage the heart over time and raise blood pressure.
On the other hand, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains has been shown to lower blood pressure.
The intricate interplay between nutrients, such as potassium which eases tension in blood vessel walls, and dietary patterns like the DASH diet, underscores the potential of nutrition as a powerful tool in preventing and managing hypertension.
Dietary Approaches to Manage High Blood Pressure

1. Moderating Sodium Intake
The link between sodium and high blood pressure is well-documented, with evidence suggesting that excessive sodium intake can significantly raise blood pressure levels. Sodium causes the body to retain water, which increases the volume of blood in the bloodstream, leading to higher blood pressure.
Hidden Sources of Sodium
Sodium lurks in many foods, often hidden and not immediately obvious:
- Processed Foods: Items like canned soups, frozen dinners, and fast food are notorious for their high sodium content.
- Condiments: Soy sauce, ketchup, salad dressings, and seasoning packets can add significant amounts of sodium to meals.
- Snacks: Chips, pretzels, crackers, and even some seemingly healthy snacks are often salted.
Practical Tips for Reducing Sodium
At Home:
- Read Labels: Pay attention to the Nutrition Information Panel when shopping. Look for lower-sodium options or those labeled with a Healthier Choice Symbol.
- Cook Smart: Use herbs and spices like garlic, ginger, or lemon zest to enhance flavor without adding salt.
- Limit Salt in Recipes: Cut back on the amount of salt called for in recipes or eliminate it altogether.
Eating Out:
- Special Requests: Ask for dishes to be made with less salt or sauces on the side.
- Taste First: Try your food before reaching for the salt shaker—often it doesn’t need extra seasoning.
By consciously moderating sodium intake through these methods, individuals can work towards better high blood pressure management as part of a comprehensive approach that includes healthy eating and lifestyle changes.
2. Increasing Potassium-Rich Foods
Potassium, an essential mineral, plays a crucial role in offsetting the harmful effects of sodium on blood pressure. It helps relax the walls of blood vessels, thereby lowering blood pressure. Ensuring a healthy balance of potassium in your diet can be instrumental in high blood pressure management.
Consider incorporating potassium-rich foods into your daily meals:
- Bananas: A convenient and affordable option, bananas are packed with potassium.
- Avocados: Besides being rich in heart-healthy fats, avocados provide a substantial amount of potassium.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale and other leafy greens are excellent sources of this vital mineral.
Remember, adopting a comprehensive lifestyle approach that emphasizes a balanced diet is crucial when managing high blood pressure. While reducing sodium intake is important, don’t overlook the benefits of increasing consumption of potassium-rich foods.
3. Following a DASH Diet
Adopting the DASH diet, short for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, is a proven strategy for high blood pressure management. This eating plan emphasizes:
- Increased intake of fruits and vegetables: These provide essential nutrients and fibers.
- Whole grains: They are rich in nutrients and fiber that help control blood pressure.
- Lean proteins: Including fish, poultry, and nuts.
- Low-fat dairy: Which supplies calcium without excessive saturated fat.
By focusing on these food groups, the DASH diet naturally reduces sodium intake, an important factor in controlling blood pressure.
It’s not just about reducing salt consumption; it’s about healthy eating as part of a comprehensive lifestyle approach.
The effectiveness of the DASH diet lies in its balanced dietary pattern rather than just isolating specific nutrients for hypertension management.
4. Choosing Magnesium-Rich Foods
Magnesium is important for regulating blood pressure.
It helps in moving calcium and potassium ions across cell membranes, which is necessary for heart rhythm and muscle contraction.
Therefore, it’s crucial to consume enough magnesium to effectively manage high blood pressure.
Here are some foods that are rich in magnesium:
- Nuts, such as almonds and cashews
- Seeds, like flaxseeds and chia seeds
- Whole grains including brown rice and oatmeal
Incorporating these foods into your diet not only helps maintain a healthier blood pressure but also provides various other health benefits due to their high nutrient content.
Remember, managing high blood pressure through healthy eating involves more than just reducing salt intake.
It’s important to focus on a balanced diet that includes nutrient-rich foods like those high in magnesium as they can greatly impact your overall health.
5. Other Nutritional Considerations (Vitamin D, Omega-3 Fatty Acids)
Healthy eating for high blood pressure management goes beyond controlling sodium and salt intake.
It involves a holistic approach to lifestyle, with a focus on a balanced diet.
Two important components of this diet are Vitamin D and Omega-3 Fatty Acids.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Hypertension
Some studies suggest that not having enough Vitamin D may increase the risk of hypertension.
Vitamin D is naturally obtained from sunlight exposure and fortified foods like milk.
So, try to get some sun in the early morning or late afternoon when it’s not too strong.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
These healthy fats can be found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
They have shown promise in helping to manage blood pressure levels. Including these fishes in your diet regularly can be beneficial.
Remember, making these dietary changes should go hand-in-hand with other lifestyle adjustments for better control of high blood pressure.
Read More: How to Calculate How Much Calories You Need A Day
Lifestyle Modifications to Support a Healthy Blood Pressure
An active lifestyle is a powerful tool in the fight against hypertension.
Regular physical activity helps lower blood pressure levels and maintain a healthy weight, both of which are crucial for heart health.
Aim for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise weekly. It could be as simple as brisk walking, cycling, or dancing.
Equally important is effective stress management. High stress levels can lead to temporary spikes in blood pressure and foster unhealthy habits like overeating, smoking, or excessive alcohol consumption.
Engage in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, meditation, or any hobby that brings joy and calmness.
Lastly, invest in adequate sleep. Sleep deprivation can upset your body’s natural balance and lead to higher blood pressure. Strive for seven to eight hours of quality sleep per night. Implementing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a peaceful sleep environment can significantly improve sleep quality.
Remember, a healthier lifestyle leads to healthier blood pressure readings. Stay committed to these changes and watch your health transform positively.
When to Seek Professional Advice

Managing high blood pressure effectively requires a good understanding of personal health needs. When should you seek professional guidance?
- Persistent high readings: If your home monitors consistently show high blood pressure, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
- Symptoms: Experiencing symptoms such as frequent headaches, chest pain, or shortness of breath warrants immediate medical attention.
A registered dietitian specializing in hypertension management can provide personalized advice tailored to individual dietary patterns and preferences.
They can also help navigate through the maze of information about hypertension and clarify any misconceptions.
It’s also important to get a comprehensive medical evaluation. High blood pressure can be a symptom of underlying health issues that need to be addressed.
A thorough check-up by a doctor will uncover these hidden causes and pave the way for targeted and effective treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding the important role of diet in controlling high blood pressure is a significant development for overall health and wellness.
Adopting healthy eating habits can effectively manage hypertension and lead to a more energetic and healthier life.
It’s crucial to note that these dietary changes are not only beneficial in the short term but also have long-term advantages for our well-being.
Keep in mind that making sustainable lifestyle modifications while seeking guidance from healthcare experts is the best way to protect ourselves from the dangers of high blood pressure.
Start taking action today to ensure a heart-healthy future.


